A filling and sealing machine is an automated packaging system designed to streamline the process of filling containers with products and sealing them for distribution. These machines fill cups or trays with products such as yogurt, soups, and other liquid foods, then seal these cups with plastic film or aluminum foil of specific thickness. In today's competitive manufacturing landscape, these machines have become essential equipment for businesses seeking to improve efficiency, maintain product quality, and reduce operational costs.
The significance of filling and sealing machines extends beyond simple automation – they represent a crucial investment in production scalability, quality consistency, and regulatory compliance. This comprehensive guide will explore the various types of filling and sealing machines, their working principles, key advantages, industry applications, and provide practical guidance for selecting the right equipment for your business needs.
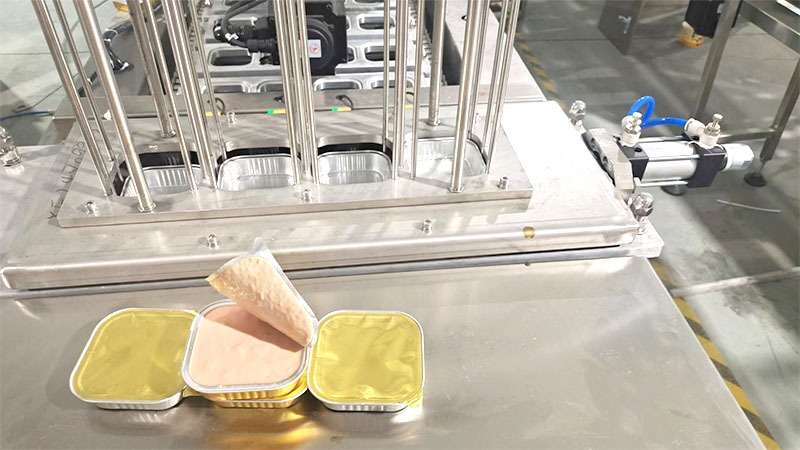
Understanding the working principle of filling and sealing machines is essential for making informed purchasing decisions and optimizing their performance in your production line.
Modern filling and sealing machines operate through sophisticated automation systems that automate the entire container filling and sealing process, significantly reducing manual labor and increasing production speed. The process typically involves several synchronized stages:
Stage 1: Container Positioning The machine automatically positions empty containers or forms them from packaging materials. Advanced sensors ensure precise alignment and detect any irregularities in container placement.
Stage 2: Product Filling Controlled dispensing systems deliver exact quantities of product into each container. The filling mechanism varies depending on product viscosity, with options including volumetric, gravimetric, or level-based filling methods.
Stage 3: Sealing Application Once filled, containers move to the sealing station where appropriate sealing materials (films, foils, or lids) are applied using heat sealing, ultrasonic sealing, or pressure-sensitive methods.
Stage 4: Quality Control Integrated inspection systems check seal integrity, fill levels, and overall package quality before products proceed to the discharge area.
Modern machines incorporate sophisticated control systems featuring touchscreen interfaces, recipe management capabilities, and real-time monitoring. These systems enable operators to adjust parameters quickly, store multiple product configurations, and maintain detailed production records for quality assurance and regulatory compliance.
The diversity of products requiring packaging has led to the development of various machine configurations, each optimized for specific applications and production requirements.
Vertical form fill seal machines are designed to produce pillow bags and can be loaded manually or automatically. These versatile machines create packages from rollstock film, making them ideal for products like snacks, powders, and granular materials. VFFS machines offer excellent flexibility in package sizes and can handle various product types with minimal changeover time.
Rotary filling and sealing machines operate around 8 stations and can process up to 40 products per minute. These high-speed machines are particularly effective for liquid and semi-liquid products requiring precise fill volumes. The rotary design ensures continuous operation while maintaining accuracy and consistency across all filling positions.
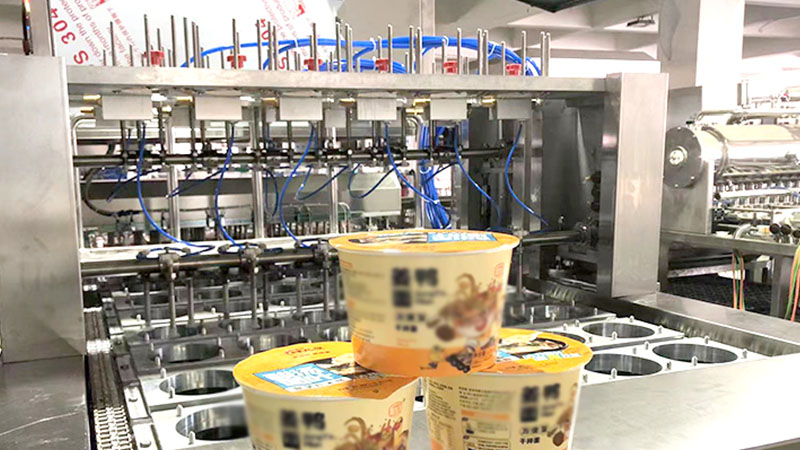
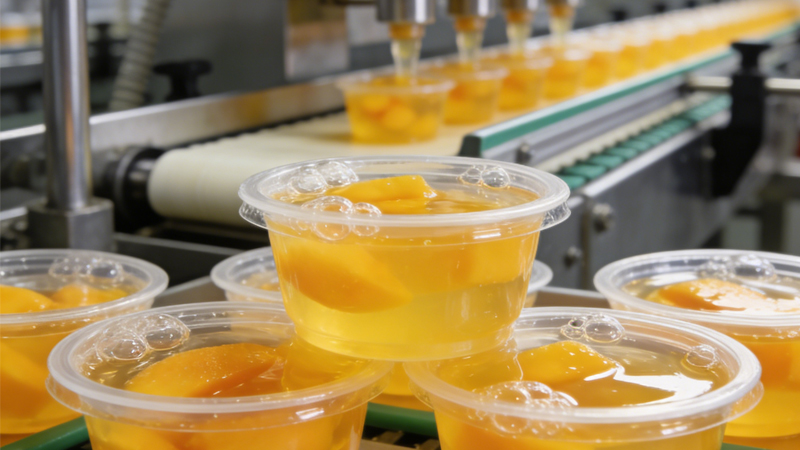
Specialized for pre-formed containers, cup filling and sealing machines are widely used in the food and pharmaceutical industries. They excel at handling products requiring precise portioning and hermetic sealing, such as yogurt, sauces, and pharmaceutical preparations.
These machines are designed for flexible packaging applications, particularly in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food products. They can handle various tube materials and sizes while providing accurate fill control and secure sealing.
Fully automatic machines require minimal operator intervention and can run continuously for extended periods. They feature advanced controls, automatic changeover capabilities, and integrated quality control systems.
Semi-automatic machines require some manual intervention but still provide significant productivity improvements over manual operations. They're ideal for medium-volume production and businesses transitioning to automation.
Manual filling and sealing equipment offers cost-effective solutions for small-scale operations while still providing consistency improvements over purely manual processes.
The adoption of filling and sealing machines brings numerous technical and operational benefits that directly impact business performance.
By automating the sealing process, production line speeds are significantly increased. This efficiency gain extends beyond simple speed improvements – automated systems eliminate bottlenecks, reduce changeover times, and enable continuous operation with minimal supervision.
Automation increases productivity with each tube filled to the same level, ensuring consistent output quality while maximizing throughput. The precision of automated systems also reduces product waste and minimizes the need for rework or quality corrections.
Reducing human error ensures consistent product quality across all production runs. Automated systems eliminate variables associated with manual operations, such as inconsistent fill levels, improper seal application, or contamination risks.
Every tube is filled and sealed according to precise specifications, maintaining uniformity that's difficult to achieve with manual processes. Advanced monitoring systems continuously verify quality parameters and alert operators to any deviations from established standards.
Reducing labor and material waste while minimizing human filling and sealing errors creates substantial cost savings over time. While the initial investment in automated equipment may be significant, the long-term operational benefits typically result in rapid return on investment.
Labor cost reduction is often the most immediate benefit, but savings from reduced waste, improved quality consistency, and decreased rejection rates contribute significantly to overall profitability. Additionally, automated systems often enable businesses to take on larger contracts or enter new markets that require higher production capacities.
Filling and sealing machines serve diverse industries, each with unique requirements and challenges that these systems address effectively.
The food industry represents the largest market for filling and sealing equipment, with applications ranging from dairy products to processed foods.
Dairy Products: Yogurt, cheese, cream, ice cream and other products packaging requires precise temperature control, sterile conditions, and hermetic sealing to maintain product freshness and safety.
Processed Foods: Pet food, frozen foods, snacks, vegetables, granular products, cereals and similar products benefit from automated packaging that maintains product integrity while ensuring attractive presentation.
Liquid Products: Beverages, sauces, and liquid foods require specialized filling systems that prevent spillage, maintain accuracy, and provide secure sealing to prevent leakage.
Various packaging formats in the pharmaceutical industry require exceptional precision, sterility, and traceability. Filling and sealing machines in pharmaceutical applications must comply with strict regulatory requirements including FDA guidelines and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Critical considerations include:
Sterile processing environments
Precise dosage control
Tamper-evident packaging
Batch tracking and documentation
Material compatibility with active ingredients
Cosmetics and daily chemical products filling and sealing applications focus on maintaining product quality while ensuring attractive packaging presentation. These products often require specialized handling due to their viscosity, pH levels, or sensitivity to contamination.
Key requirements include:
Aesthetic package appearance
Product stability maintenance
Contamination prevention
Precise fill accuracy for premium products
Compatibility with various container materials
Beyond the primary sectors, filling and sealing machines serve numerous other applications:
Agricultural Products: Seeds, fertilizers, and agricultural chemicals require secure packaging that prevents moisture ingress and contamination.
Industrial Products: Lubricants, adhesives, and chemical products need specialized filling systems that handle hazardous materials safely while maintaining worker safety.
Choosing the right filling and sealing machine requires careful consideration of multiple factors that will impact long-term operational success.
Begin by evaluating current and projected production requirements. Consider:
Daily, weekly, and seasonal production volumes
Peak capacity requirements
Future growth projections
Available production time windows
Flexibility requirements for multiple products
Different products require specific handling capabilities:
Viscosity Considerations: Low-viscosity liquids require different filling mechanisms than thick creams or gels. Ensure the selected machine can handle your product's flow characteristics.
Temperature Requirements: Some products require heated or chilled handling, necessitating specialized equipment features.
Particulate Content: Products containing particles or chunks need filling systems designed to handle these characteristics without damage or separation.
Evaluate compatibility with your desired packaging formats:
Container materials (plastic, glass, metal)
Package sizes and shapes
Closure types (heat seal, mechanical, pressure-sensitive)
Label and coding requirements
Develop a comprehensive budget that includes:
Initial equipment cost
Installation and commissioning expenses
Training requirements
Ongoing maintenance costs
Spare parts inventory
Potential facility modifications
Select suppliers based on:
Technical expertise and industry experience
After-sales support capabilities
Training program quality
Spare parts availability
Financial stability and longevity
Customer references and case studies
The filling and sealing machine industry continues to evolve, driven by technological advancement and changing market demands.
Modern machines increasingly incorporate Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities, enabling:
Remote monitoring and diagnostics
Predictive maintenance scheduling
Real-time production optimization
Data analytics for process improvement
Integration with enterprise resource planning systems
Environmental concerns drive innovation in:
Biodegradable packaging material compatibility
Reduced material usage optimization
Energy-efficient operation modes
Recyclable packaging format support
Waste reduction technologies
Future machines emphasize modular construction for:
Simplified upgrades and expansions
Reduced maintenance complexity
Improved flexibility for product changes
Cost-effective scalability options
Standardized component interfaces
Emerging technologies include:
Vision inspection systems
Artificial intelligence-based quality assessment
Real-time contamination detection
Automated rejection and sorting systems
Blockchain integration for traceability
Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance, extends equipment life, and maintains product quality standards.
Cleaning Protocols:
Thorough cleaning of product contact surfaces
Sanitization according to industry standards
Inspection of sealing elements for wear or damage
Verification of proper lubrication levels
Operational Checks:
Calibration verification for filling accuracy
Seal quality inspection
Temperature monitoring for heated systems
Pressure verification for pneumatic components
Weekly Tasks:
Detailed component inspection
Wear part assessment and replacement
Control system backup procedures
Safety system functionality tests
Monthly Activities:
Comprehensive cleaning and sanitization
Calibration verification and adjustment
Spare parts inventory review
Performance optimization assessment
Annual Requirements:
Complete system overhaul
Professional service and inspection
Software updates and upgrades
Compliance verification and documentation
Filling Accuracy Issues:
Check calibration settings
Inspect dispensing components for wear
Verify product temperature consistency
Examine flow path for obstructions
Sealing Problems:
Verify sealing temperature settings
Check sealing element condition
Confirm proper material specifications
Assess pressure and timing parameters
Understanding the financial impact of filling and sealing machine investments helps justify purchases and optimize operational decisions.
Equipment Costs:
Base machine pricing varies significantly by capacity and features
Installation and commissioning expenses typically add 10-20% to equipment costs
Training programs ensure proper operation but require budget allocation
Facility modifications may be necessary for proper installation
Supporting Infrastructure:
Utilities (compressed air, electricity, water)
Material handling equipment
Quality control instrumentation
Safety systems and compliance measures
Labor Cost Reduction: Automation significantly reduces direct labor requirements while enabling workers to focus on higher-value activities. The elimination of repetitive manual tasks also reduces worker fatigue and injury risks.
Quality Improvement Benefits: Consistent product quality reduces rejection rates, customer complaints, and warranty costs. Improved package integrity extends shelf life and reduces spoilage losses.
Productivity Gains: Higher production speeds and reduced downtime enable increased throughput without proportional increases in overhead costs. This scalability supports business growth without linear cost increases.
Operational Efficiency: Reduced material waste, optimized resource utilization, and improved process control contribute to lower overall production costs and higher profit margins.
Payback Period Analysis: Calculate the time required to recover the initial investment through operational savings. Most filling and sealing machines achieve payback within 12-36 months, depending on production volumes and labor cost savings.
Net Present Value Assessment: Consider the time value of money when evaluating long-term benefits. Include factors such as increased production capacity, quality improvements, and reduced maintenance costs over the equipment's useful life.
Filling and sealing machines represent a critical investment in modern manufacturing operations, offering substantial benefits in efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. The technology has evolved to address diverse industry needs while providing scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes.
When choosing filling and sealing equipment, prioritize:
Production Requirements: Ensure capacity alignment with current and future needs
Product Compatibility: Verify the machine can handle your specific products effectively
Quality Standards: Select equipment that meets or exceeds your industry's quality requirements
Vendor Support: Choose suppliers with proven track records and comprehensive support capabilities
Total Cost of Ownership: Consider long-term operational costs, not just initial purchase price
The filling and sealing machine industry continues to advance, driven by automation technologies, sustainability requirements, and evolving consumer demands. Businesses investing in modern equipment position themselves advantageously for future growth and competitive success.
Conduct a thorough needs assessment to understand your specific requirements and constraints
Evaluate multiple suppliers to ensure you receive the best combination of technology, service, and value
Plan for proper training and maintenance to maximize equipment performance and longevity
Consider future growth and flexibility when making selection decisions
Develop comprehensive ROI models to justify investments and measure success
The investment in quality filling and sealing equipment pays dividends through improved efficiency, enhanced product quality, and reduced operational costs. By carefully evaluating options and selecting appropriate technology, businesses can achieve significant competitive advantages while positioning themselves for sustainable long-term growth.
Modern filling and sealing machines are not merely packaging equipment – they are strategic assets that enable businesses to scale operations, maintain quality standards, and adapt to changing market demands. The key to success lies in making informed decisions based on thorough analysis of needs, technology options, and long-term business objectives.
Your Name*
Your Email*















*We respect your confidentiality and all information are protected.